Cable Gland – Types, Sizes, Parts & Industrial Applications
Intro about what a cable gland is
A cable gland is a mechanical device used to securely attach and seal electrical cables where they enter equipment, enclosures, or control panels. It prevents dust, moisture, and gas ingress while providing strain relief and mechanical stability to the cable.
Cable glands are widely used in industrial, commercial, and hazardous environments such as oil and gas plants, power stations, marine installations, mining operations, and automation systems. Proper sealing and secure termination help maintain electrical safety and reliable system performance.
Available in different designs, materials, and sizes, cable glands are selected based on cable type, outer diameter, and environmental conditions. Choosing the correct cable gland helps prevent cable damage, loose fittings, and safety risks in demanding industrial applications.
Types of Cable Glands
The following are the six most commonly used cable gland types in industrial and commercial applications.

Single Compression
Cable Glands
for unarmoured cables

Double Compression
Cable Glands
for armoured cables

Armoured
Cable Glands
steel wire armoured (SWA) cables

Unarmoured
Cable Glands
cables without metallic armour

Flameproof (Explosion-Proof)
Cable Glands
hazardous areas

Waterproof / Weatherproof
Cable Glands
for outdoor use
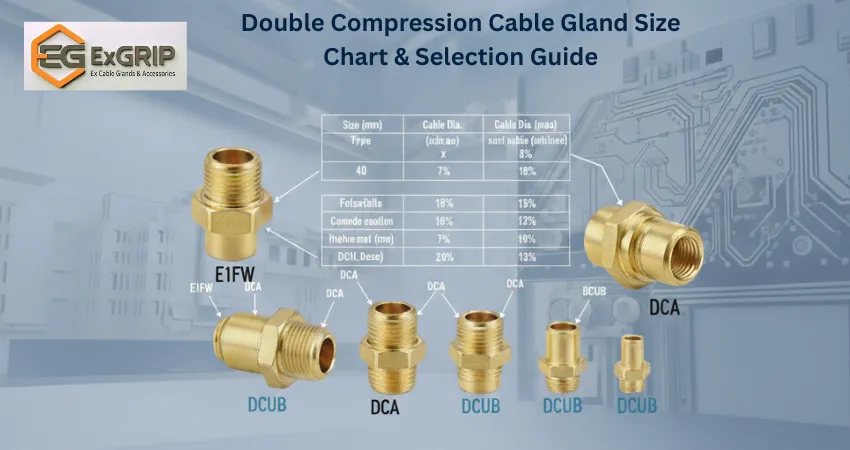
Cable Gland Sizes & Gland Chart
Cable gland size selection is based on the outer diameter (OD) of the cable to ensure proper sealing, mechanical grip, and long-term safety. Choosing the correct cable gland size is critical, as an incorrect size can lead to loose fittings, water ingress, poor strain relief, or electrical faults.
Cable gland sizes are generally specified in millimetres (mm) and matched to a specific clamping range. Engineers typically refer to a gland chart to identify the correct gland size based on cable OD, thread type, and application requirements. Common thread standards include Metric, PG, NPT, and BSP, depending on regional and project specifications.
| CABLE GLAND TYPES/SERIES | ||
|---|---|---|
| FOR UNARMOURED CABLE | ||
| Series | Compression Type | Type |
| A2F Series | Single Compression | Standard |
| SCU Series | Single Compression | Standard |
| SCUB Series | Single Compression | Barrier |
| DCU Series | Double Compression | Standard |
| DCUB Series | Double Compression | Barrier |
| CABLE GLAND TYPES/SERIES | ||
|---|---|---|
| FOR ARMOURED CABLE | ||
| Series | Compression Type | Type |
| SCA Series | Single Compression | Standard |
| SCAB Series | Single Compression | Barrier |
| E1FW Series | Double Compression | Standard |
| DCA Series | Double Compression | Standard |
| DCAB Series | Double Compression | Barrier |
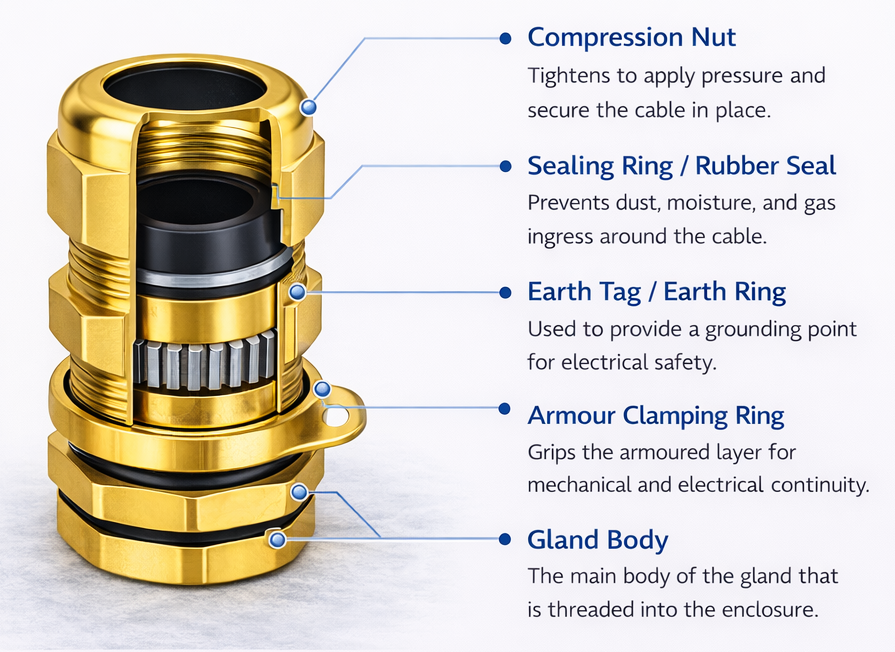
Cable Gland Parts Name & Functions
A cable gland consists of several precisely engineered components that work together to provide sealing, mechanical grip, and electrical safety. Understanding the different cable gland parts name and their functions helps ensure correct installation and long-term reliability, especially in industrial and hazardous environments.
Cable Gland Accessories
Cable gland accessories are essential components used to ensure proper installation, sealing, and safety of cable entries. These accessories help adapt cable glands to different enclosure sizes, maintain ingress protection, and support secure mounting in industrial and hazardous environments.
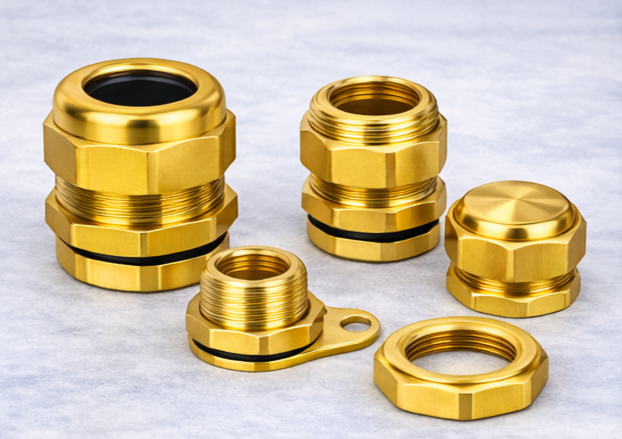

Reducer
Used to reduce the enclosure entry size so a larger cable gland can be fitted securely.
Adapter
Converts one thread type or size to another, such as Metric, PG, NPT, or BSP.
Stopping Plug
Seals unused cable entry holes to prevent dust, moisture, and gas ingress.
Locknut
Secures the cable gland firmly inside the enclosure and prevents loosening.
Earth Tag / Earth Ring
Provides reliable earthing continuity for armoured cable installations.
Cable Gland Applications
Cable glands are used across a wide range of industries to ensure safe cable entry, reliable sealing, and long-term electrical performance. Their ability to protect cables from environmental and mechanical damage makes them essential in both standard and hazardous installations.

Oil & Gas
Used in refineries, offshore platforms, and processing plants where explosion-proof and flameproof cable protection is critical.

Power Plants & Energy
Protect power and control cables in high-temperature, high-voltage, and demanding electrical environments.

Marine & Offshore
Provide corrosion resistance and watertight sealing against moisture and saltwater exposure.

Mining Operations
Heavy-duty armoured cable glands designed to withstand vibration, dust, and harsh working conditions.

Industrial Automation
Ensure safe cable management, sealing, and strain relief in control panels and automated systems.

Chemical & Renewable Energy
Deliver reliable performance in chemical plants, petrochemical units, and renewable energy installations.
How to Select the Right Cable Gland
Selecting the correct cable gland is essential for ensuring safety, proper sealing, and long-term performance of electrical installations. The right choice depends on the cable construction, operating environment, size requirements, and material suitability. Armoured and unarmoured cables require different gland types, and accurate measurement of the cable’s outer diameter (OD) is critical to ensure a secure fit.
Installation conditions also play a major role in cable gland selection. For outdoor, dusty, or wet environments, cable glands with higher ingress protection ratings such as IP66, IP67, or IP68 are recommended. In hazardous areas where flammable gases or dust may be present, certified flameproof or explosion-proof cable glands should be used to meet safety standards.
Material selection further impacts performance and durability. Brass cable glands are commonly used for industrial applications due to their strength and corrosion resistance, stainless steel glands are ideal for marine and corrosive environments, and nylon glands are suitable for light-duty or indoor use. By considering cable type, size, environment, and material, the correct cable gland can be selected to ensure reliable sealing, mechanical stability, and long service life.

Identify Cable
Type
Determine whether the cable is armoured or unarmoured to select the appropriate cable gland type.
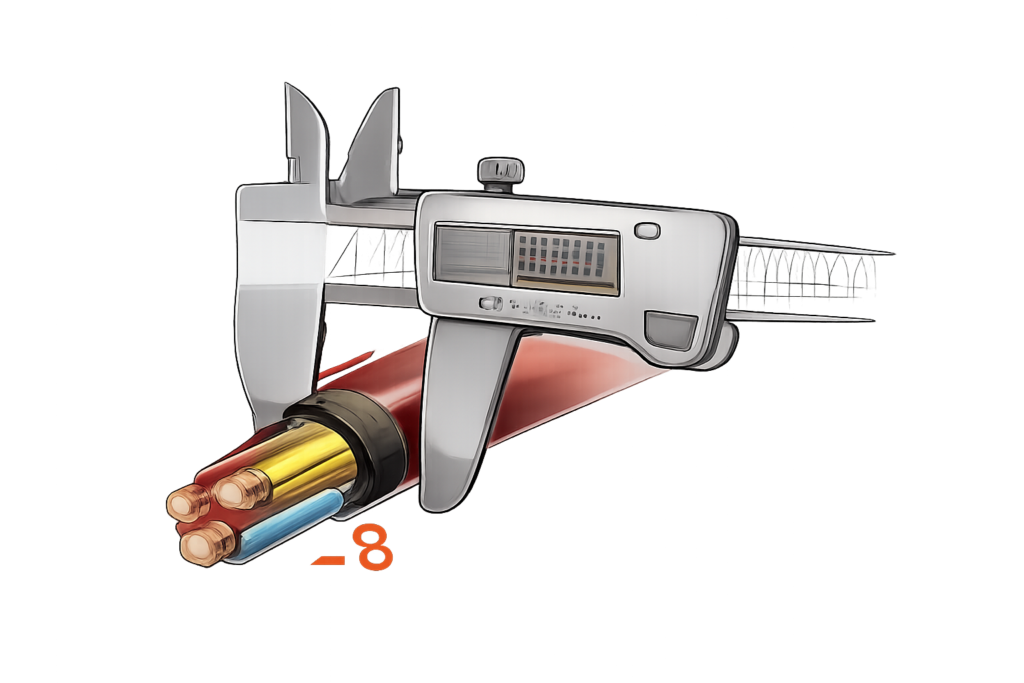
Measure Cable
Diameter
Measure the outer diameter (OD) of the cable accurately and match it with the correct gland size using a gland chart.

Consider Installation Environment
Select cable glands based on environmental conditions such as indoor, outdoor, wet, dusty, or hazardous areas.

Choose Gland
Material
Choose brass, stainless steel, or nylon cable glands depending on mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and application needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a cable gland used for?
A cable gland is used to securely connect and seal electrical cables where they enter equipment or enclosures. It provides protection against dust, moisture, vibration, and mechanical stress while ensuring electrical safety.
How do I choose the correct cable gland size?
The correct cable gland size is selected based on the cable’s outer diameter (OD). Measuring the OD accurately and matching it with a gland chart ensures proper sealing, strain relief, and secure installation.
What is the difference between single compression and double compression cable glands?
Single compression cable glands seal only the outer sheath of the cable and are mainly used for unarmoured cables. Double compression cable glands provide sealing on both the inner and outer sheath, making them suitable for armoured cables and heavy-duty applications.
Which material is best for cable glands?
Brass cable glands are commonly used for industrial applications due to strength and corrosion resistance. Stainless steel cable glands are ideal for marine and corrosive environments, while nylon cable glands are suitable for indoor and light-duty use.
Are cable glands required for hazardous areas?
Yes, hazardous areas require certified flameproof or explosion-proof cable glands that comply with ATEX or IECEx standards to prevent flame or gas transmission and ensure safety.
Industry Insights & Updates