Selecting the correct cable gland size is one of the most critical steps in any electrical installation—especially in industrial, outdoor, and hazardous environments. A cable gland is not just a mechanical fitting; it directly affects IP rating, sealing performance, and explosion protection.
Many electrical failures occur not due to poor product quality, but due to incorrect cable gland sizing. In this blog, we explain what is a cable gland, how different electrical cable gland types work, the importance of cable gland parts, and how wrong sizing can compromise safety—even when certified products are used.
What Is a Cable Gland?
A cable gland is a mechanical device used to secure and seal the end of an electrical cable where it enters an enclosure, panel, or equipment.
The main functions of a cable gland are:
Mechanical cable retention
Environmental sealing against dust, water, and gases
Strain relief and vibration resistance
Electrical continuity and earthing (for armoured cables)
Explosion protection in hazardous areas
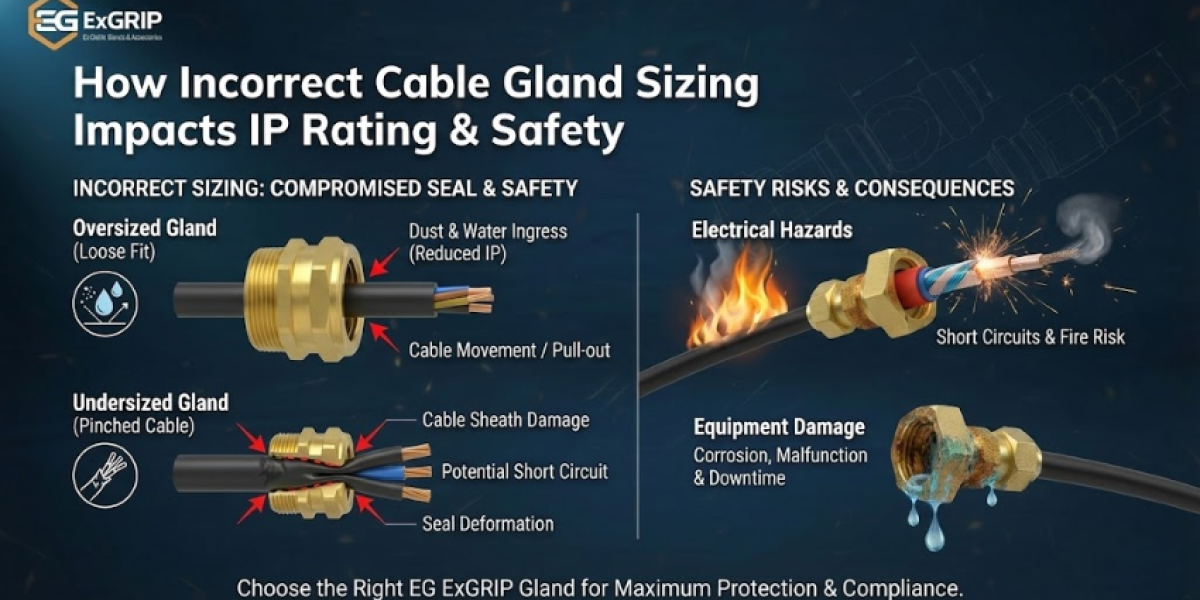
If the cable gland size does not match the cable, these functions fail.
Why Cable Gland Size Matters More Than You Think
Cable gland sizing is based on the outer diameter (OD) of the cable, not only on core count or conductor size. Selecting the wrong size leads to:
Poor compression of sealing rings
Reduced IP protection
Mechanical instability
Loss of explosion-proof integrity
This is why installers rely on a gland chart before finalizing any installation.
How Incorrect Cable Gland Sizing Affects IP Rating & Electrical Safety
| Cable Gland Type | Suitable Cable Type | Typical IP Rating Range | Sealing Method | Effect of Incorrect Gland Sizing | Recommended Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Compression Cable Gland | Unarmoured cables | IP54 – IP66 | Seals outer cable sheath only | Loose sealing allows dust and water ingress, reducing IP protection | Indoor panels, control cabinets |
| Double Compression Cable Gland | Armoured cables | IP66 – IP68 | Seals both inner and outer sheath | Incorrect sizing affects sealing and armour clamping, compromising IP rating | Outdoor installations, industrial plants |
| Flameproof / ATEX Cable Gland | Unarmoured & armoured cables (hazardous areas) | IP66 – IP68 | Explosion-proof sealing with flame path control | Wrong size voids IP rating and explosion protection certification | Oil & gas, chemical, hazardous zones |
| Brass Cable Gland | Armoured & unarmoured cables | IP65 – IP68 | Metallic body with elastomeric seals | Poor compression due to wrong size leads to seal failure | Industrial & corrosive environments |
| Nylon / Plastic Cable Gland | Unarmoured cables | IP54 – IP66 | Plastic body with rubber sealing ring | Incorrect sizing causes early wear and reduced IP protection | Light-duty indoor applications |
Explosion Protection Risks Due to Wrong Cable Gland Size
In hazardous environments, flameproof and explosion-proof cable glands are designed to:
Prevent flame propagation
Control gas entry
Maintain pressure containment
However, incorrect gland sizing can lead to serious safety issues:
Common Risks
| Risk | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Improper Flame Path | Flame path dimensions do not meet safety requirements | Increased risk of ignition or explosion |
| Gaps in Sealing Chambers | Seals fail to compress properly | Dust, water, or gas can enter, compromising safety |
| Loss of Explosion Containment | Pressure and flameproofing fail | Equipment may no longer be safe for hazardous zones |
| Invalid Certification | ATEX or IECEx certification is void | Non-compliance with industry safety standards |
Note: Even the best-designed explosion-proof cable gland will fail if the size does not match the cable outer diameter or the enclosure. Always verify cable measurements and the gland’s clamping range before installation.
Electrical Cable Gland Chart
| CABLE GLAND TYPES/SERIES | ||
|---|---|---|
| FOR UNARMOURED CABLE | ||
| Series | Compression Type | Type |
| A2F Series | Single Compression | Standard |
| SCU Series | Single Compression | Standard |
| SCUB Series | Single Compression | Barrier |
| DCU Series | Double Compression | Standard |
| DCUB Series | Double Compression | Barrier |
| FOR ARMOURED CABLE | ||
| Series | Compression Type | Type |
| SCA Series | Single Compression | Standard |
| SCAB Series | Single Compression | Barrier |
| E1FW Series | Double Compression | Standard |
| DCA Series | Double Compression | Standard |
| DCAB Series | Double Compression | Barrier |
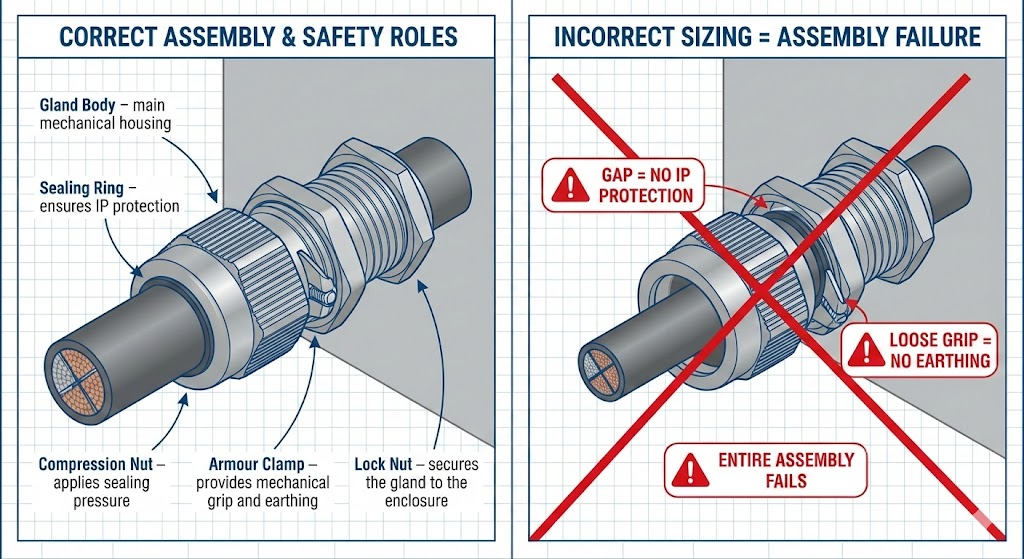
Cable Gland Parts Name and Their Role in Safety
Conclusion & Call-to-Action
Incorrect cable gland sizing is a silent risk that affects IP rating, mechanical integrity, and explosion protection. Even certified products fail if the size is wrong.
In this blog, we covered:
What is a cable gland
Electrical cable gland types
Cable gland parts name and function
Importance of gland chart usage
Risks of incorrect sizing using a 4 core cable gland size chart
Correct cable gland selection ensures long-term safety, compliance, and performance.
How to Order Cable Glands from Us


Contact Us:


FAQs
What is a cable gland used for?
A cable gland secures and seals cables entering electrical equipment, providing mechanical protection, IP sealing, and electrical safety.
Can incorrect cable gland size affect IP rating?
Yes. Wrong sizing prevents proper seal compression, allowing dust and water ingress even in IP-rated glands.
Why is outer diameter important in cable gland selection?
Cable gland sealing depends on cable outer diameter, not just core count or conductor size.
Are gland charts always accurate?
Gland charts are guides. Actual cable OD and application conditions must always be verified.
Which cable gland type is best for safety?
Double compression and flameproof cable glands are preferred for armoured cables and hazardous areas when sized correctly.